Sorting, Grouping, and Filtering for List Binding
Initial Sorting, Grouping and Filtering for List Binding
To provide initial sorting and grouping in an XML view, proceed as follows:
<mvc:View
controllerName="sap.ui.sample.App"
xmlns="sap.m"
xmlns:l="sap.ui.layout"
xmlns:mvc="sap.ui.core.mvc">
<List items="{ path: '/companies',
sorter: { path: 'county', descending: false, group: '.getCounty'},
groupHeaderFactory: '.getGroupHeader'}">
<items>
<StandardListItem
title="{name}"
description="{city}"
/>
</items>
</List>
</mvc:View>The this context of a group header factory function is generally set
to the control (or managed object) that owns the binding. However, in XML views, the
reference to the group header factory is done in the view controller by putting a
dot (.) in front of the name of the group header factory function
({ groupHeaderFactory:'.myGroupHeader' }). In this case, the
group header factory's this context is bound to the controller.
The list uses a sorter which sorts the list of companies in ascending order by the
county column. It also groups its rows using the
App.controller's getCounty method to provide the captions and the
getGroupHeader function to provide non-standard group header
controls, as shown here:
sap.ui.define([
"sap/ui/core/mvc/Controller",
"sap/ui/model/json/JSONModel",
"sap/m/GroupHeaderListItem "
], function (Controller, JSONModel, GroupHeaderListItem) {
"use strict";
return Controller.extend("sap.ui.sample.App", {
onInit : function () {
…
},
getCounty: function(oContext) {
return oContext.getProperty('county');
},
getGroupHeader: function(oGroup) {
return new GroupHeaderListItem({
title : oGroup.key
}
);
},
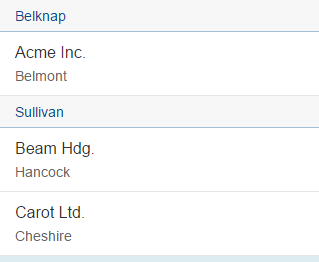
});As you can see, getCounty generates the key for a division into
groups as well as a group caption, which in this case is the county of the current
companies. getGroupHeader serves as a group header factory
function. After sorting and grouping, the company list looks like this:
The following XML snippet provides initial filtering:
<mvc:View
controllerName="sap.ui.sample.App"
xmlns="sap.m"
xmlns:l="sap.ui.layout"
xmlns:mvc="sap.ui.core.mvc">
<List items="{ path: '/companies',
filters: [{path: 'city', operator: 'StartsWith', value1: 'B'},
{path: 'revenue', operator: 'LT', value1: 150000000}]}">
<items>
<StandardListItem
title="{name}"
description="{city}"
/>
</items>
</List>
</mvc:View>The example shown here will only display companies whose city name begins with a 'b' and whose revenue is less than 150 million. As you can see, you can provide more than one filter, each of which may refer to different columns using different filter operators. For a complete list of permitted filter operators, see sap.ui.model.FilterOperator in the API Reference part of the Demo Kit.
As shown below, initial sorting, grouping and filtering can of course also be provided using JavaScript.
You can define a sorter and/or filters:
sap.ui.define([
"sap/ui/model/Sorter",
"sap/ui/model/Filter"
], function(Sorter, Filter) {
//returns group header captions
var fnGetCounty = function(oContext) {
return oContext.getProperty('county');
}
var oSorter = new Sorter({
path: 'county',
descending: false,
group: fnGetCounty});
var oFilterCity = new Filter("city",
sap.ui.model.FilterOperator.StartsWith, "B"),
oFilterRevenue = new sap.ui.model.Filter("revenue",
sap.ui.model.FilterOperator.LT, 150000000);
);
});
You can pass sorters and filters to the list binding:
var oList = new sap.m.List({
items: {path: "/companies", template: oItemTemplate,
sorter: oSorter, filters:[oFilterCity, oFilterRevenue]
}
});You can also use the other list binding possibilities (for example
bindAggregation or bindItems) and provide the
sorter and filters as parameters.
Manual Sorting and Filtering for List Binding
You can sort or filter data manually after the list binding is complete by getting the corresponding binding and calling the sort/filter function:
// manual sorting
oList.getBinding("items").sort(oSorter);
// manual filtering
oList.getBinding("items").filter([oFilterCity, oFilterRevenue]);
getBinding requires the name of the bound list. In this example,
we are looking at the items of the sap.m.List
control.
For more information about the various sorting and filter methods and operators, see the documentation for Filter, Sorter, and Filter operations under sap.ui.model in the API Reference part of the Demo Kit.
Using Complex Syntax to Add Filters and Sorters
Complex syntax can be used to add filters and sorters for list binding. One or multiple objects can be defined.
<table:Table rows="{
path: '/table',
filters: [{
path: 'field3',
operator: 'EQ',
value1: 'test'
}],
sorter: [{
path: 'field1',
descending: false
}, {
path: 'field2',
descending: true
}]
}">
...
</table:Table>