Step 14: Custom CSS and Theme Colors
Preview
As stated in the Compatibility Rules, the HTML and CSS generated by SAPUI5 is not part of the public API and may change in patch and minor releases. If you decide to override styles, you need to test and update your modifications each time SAPUI5 is updated. A prerequisite for this is that you have control over the version of SAPUI5 being used, for example in a standalone scenario. This is not possible when running your app in the SAP Fiori launchpad where SAPUI5 is centrally loaded for all apps. As such, SAP Fiori launchpad apps should not override styles.
Coding
You can view and download all files at Walkthrough - Step 14.
webapp/css/style.css (New)
html[dir="ltr"] .myAppDemoWT .myCustomButton.sapMBtn {
margin-right: 0.125rem
}
html[dir="rtl"] .myAppDemoWT .myCustomButton.sapMBtn {
margin-left: 0.125rem
}
.myAppDemoWT .myCustomText {
display: inline-block;
font-weight: bold;
}
We create a folder css which will contain our CSS files. In a new style definition file inside the
css folder we create our custom classes combined with a custom namespace class. This makes sure that the styles
will only be applied on controls that are used within our app.
A button has a default margin of 0 that we want to override: We add a custom margin of 2px (or
0.125rem calculated relatively to the default font size of 16px) to the button with the style
class myCustomButton. We add the CSS class sapMBtn to make our selector more specific: in CSS, the
rule with the most specific selector "wins".
For right-to-left (rtl) languages, like Arabic, you set the left margin and reset the right margin as the app display is inverted. If you only use standard SAPUI5 controls, you don't need to care about this, in this case where we use custom CSS, you have to add this information.
In an additional class myCustomText we define a bold text and set the display to inline-block. This
time we just define our custom class without any additional selectors. We do not set a color value here yet, we will do this in the
view.
webapp/manifest.json
...
"sap.ui5": {
...
"rootView": {
...
},
"resources": {
"css": [
{
"uri": "css/style.css"
}
]
}
}In the resources section of the sap.ui5 namespace,
additional resources for the app can be loaded. We load the CSS styles by defining a
URI relative to the component. SAPUI5 then adds this
file to the header of the HTML page as a <link> tag, just
like in plain Web pages, and the browser loads it automatically.
webapp/view/App.view.xml
<mvc:View controllerName="ui5.walkthrough.controller.App" xmlns="sap.m" xmlns:mvc="sap.ui.core.mvc" displayBlock="true"> <Shell> <App class="myAppDemoWT"> <pages> <Page title="{i18n>homePageTitle}"> <content> <Panel headerText="{i18n>helloPanelTitle}" class="sapUiResponsiveMargin" width="auto"> <content> <Button text="{i18n>showHelloButtonText}" press=".onShowHello" class="myCustomButton"/> <Input value="{/recipient/name}" valueLiveUpdate="true" width="60%"/> <FormattedText htmlText="Hello {/recipient/name}" class="sapUiSmallMargin sapThemeHighlight-asColor myCustomText"/> </content> </Panel> </content> </Page> </pages> </App> </Shell> </mvc:View>
The
app control is configured with our custom namespace class
myAppDemoWT. This class has no styling rules set and is used in
the definition of the CSS rules to define CSS selectors that are only valid for this
app.
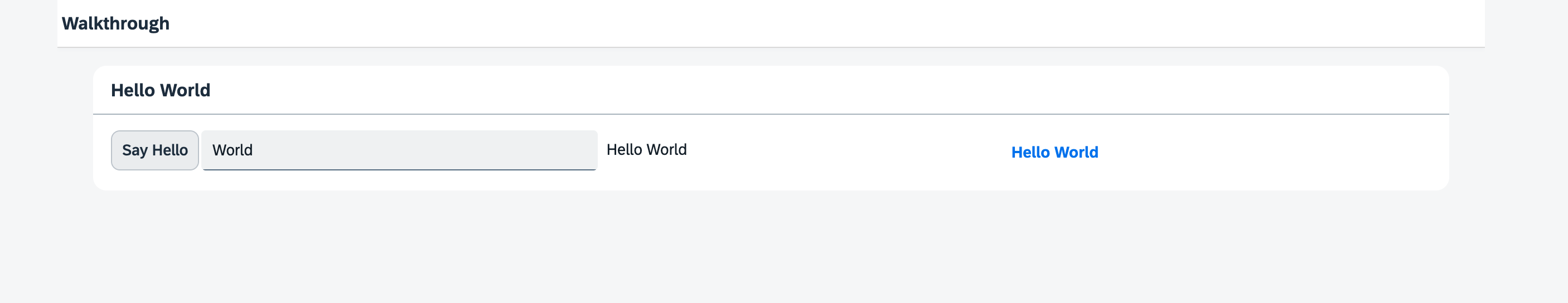
We add our custom CSS class to the button to precisely define the space between the button and the input field. Now we have a pixel-perfect design for the panel content.
To highlight the output text, we use a
FormattedText control which can be styled individually, either
by using custom CSS or with HTML code. We add our custom CSS class
(myCustomText) and add a theme-dependent CSS class to set the
highlight color that is defined in the theme.
The actual color now depends on the selected theme which ensures that the color always fits to the theme and is semantically clear. For a complete list of the available CSS class names, see CSS Classes for Theme Parameters.
Conventions
-
Do not specify colors in custom CSS but use the standard theme-dependent classes instead.
Parent topic: Walkthrough Tutorial (JavaScript)
Previous: Step 13: Margins and Paddings
Next: Step 15: Nested Views