Routing and Navigation
You use routing in the following cases:
-
Enable users to navigate back using the browser history, for example, the Back button of the browser or a physical back button on mobile devices.
-
Enable bookmarks and deep links to pages inside an app; this means that you can start the app and resume the bookmarked state.
-
Pass on data via the hash to application logic.
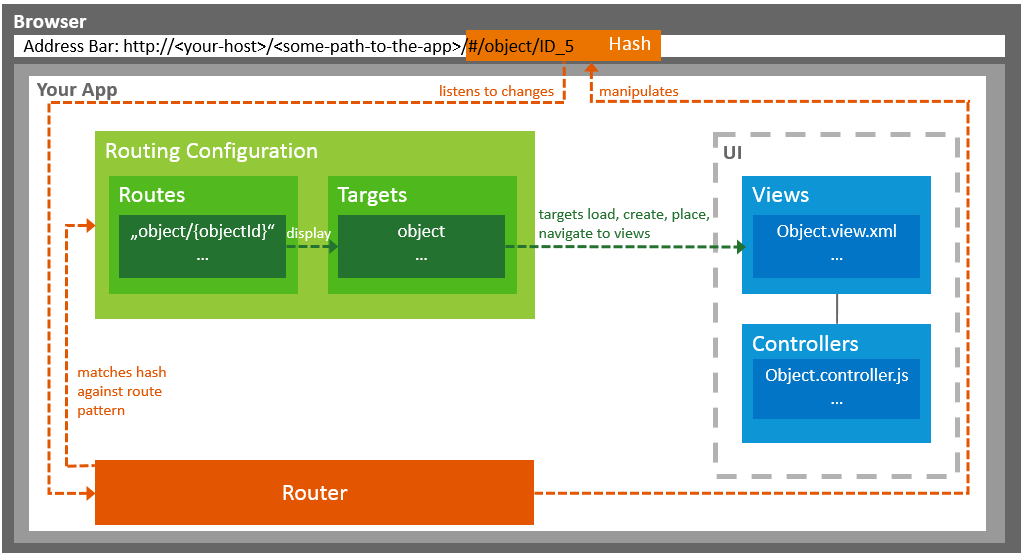
In SAPUI5, navigation and routing is implemented using a "router" to forward the hash change and the data in the hash to one or more views of the app.
You use routes to notify your application that the hash has changed to a certain value. For each route, you define the pattern that can be used in the app implementation.
With targets, you define where a view or a component is loaded and where the view or component is shown on the UI. By referring to one or multiple targets in a route's definition, you can load and show the views or components once the route's pattern matches the current hash.
You configure routing in SAPUI5 in the descriptor
file (manifest.json) (see Manifest (Descriptor for Applications, Components, and Libraries)) or in the
Component.js file (see Components ) to have it available globally
throughout your app, but you can also define routes and targets locally by calling the
constructors of the classes, for example under the sap.ui.core.routing
and sap.m.routing namespaces.
You can also define only routes or only targets, but then just have to make sure that you implement the counterpart elsewhere.